Cell viability assay using tetrazolium salt
Cellvia Instructions Guide

Cellvia Principle
What is tetrazolium salt?
Tetrazolium salt has 3 aromatic rings connected.
It is a general term for heterocyclic compound, and it is a reduced type compound or
It is easily reduced by enzymes and causes color development. Generally
It has the structure shown in the figure on the right, and the bonded aromatic ring
Depending on the type, solubility in aqueous solution and absorption spectrum are different.
is.
Structure of tetrazolium salt 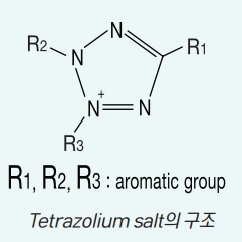
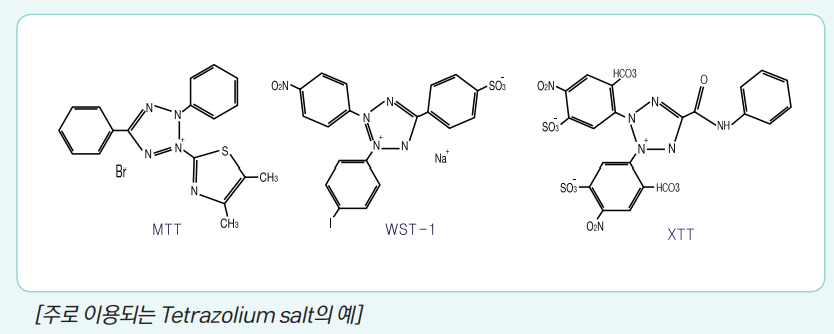
[Examples of mainly used tetrazolium salt]
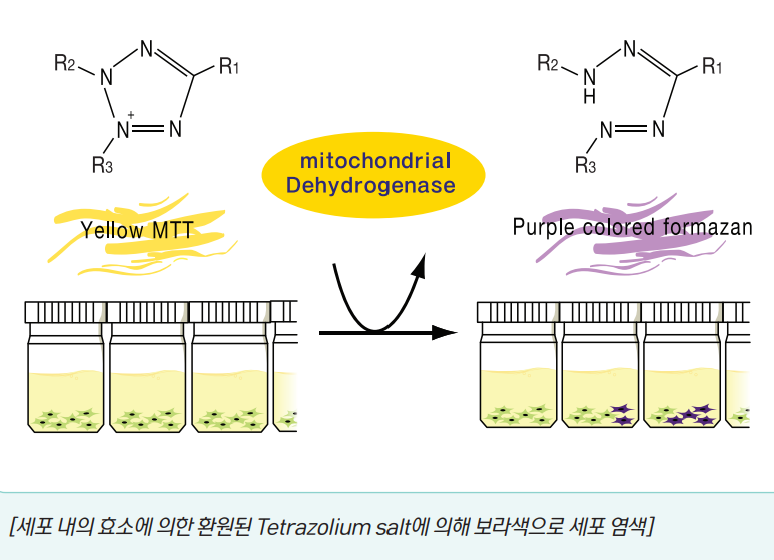
[Cell staining purple by Tetrazolium salt reduced by intracellular enzyme]
Cellvia Assay Principle
The 4-nitrogen tetrazole moiety of the tetrazolium salt is a dehydrogenase
It is easily reduced by enzymes such as formazan and converted to colored formazan.
Based on this principle, the activity of mitochondrial NADH-dehydrogenase in cells is measured.
If used in the definition, it can be applied to cytotoxicity and cell proliferation assays with high sensitivity.
can. Among tetrazolium salts, it is the most widely used in relation to cell viability test.
The one used is MTT (3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium
bromide), the general reaction principle is:
MTT-Advantages and Limitations
Everyone must have experienced it at least once in an experiment dealing with cells.
MTT assay is low cost for all cell types
Although it has the advantage of being able to measure with
There are factors.
Due to the above inconveniences, it is more sensitive and convenient
A tetrazolium salt that can be used as a method is required.
As a result, water solubility such as MTS, XTT, and WST
tetrazolium salt gradually replaces MTT
Becoming a new standard for viability assays
there is.
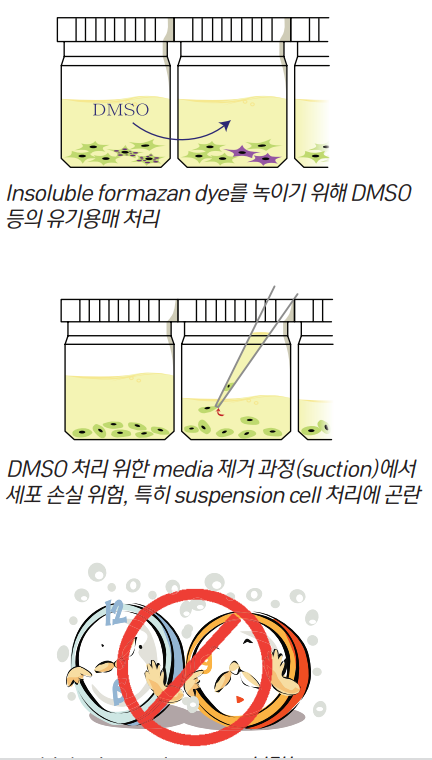
DMSO to dissolve insoluble formazan dye
Treatment of organic solvents such as
Multiple time point assay not possible
In the media removal process (suction) for DMSO treatment
Risk of cell loss, especially difficult to handle suspension cells
For cells with low metabolic activity, such as blood cells
high density of cells.